
Medical laboratory proffession (Biomedical science)
In the Republic of Croatia, biomedical science is practised across approximately 30 types of specialized laboratories, including:
laboratory
laboratory
laboratory
laboratory
laboratory
laboratory
laboratory
laboratory
laboratory
laboratory
laboratory
laboratory
laboratory
laboratory
laboratory
laboratory
laboratory
laboratory
laboratory
laboratory
laboratory
laboratory
laboratory
laboratory
laboratory
laboratory
laboratory
laboratory
laboratory
+ University laboratories
+ Veterinary laboratories
+ Pharmaceutical industry laboratories
+ Food industry laboratories
The primary professionals responsible for diagnostic procedures and laboratory analyses are biomedical scientists with master's or bachelor's degrees, as well as qualified laboratory technicians, some of whom hold additional specializations (currently, for example, in transfusion medicine and cytodiagnostics).
They work both independently and collaboratively with various experts and specialists across all areas of biomedical science. This teamwork demands a high level of expertise, effective collaboration, and mutual respect among all professionals to ensure the highest standards of quality in laboratory operations.
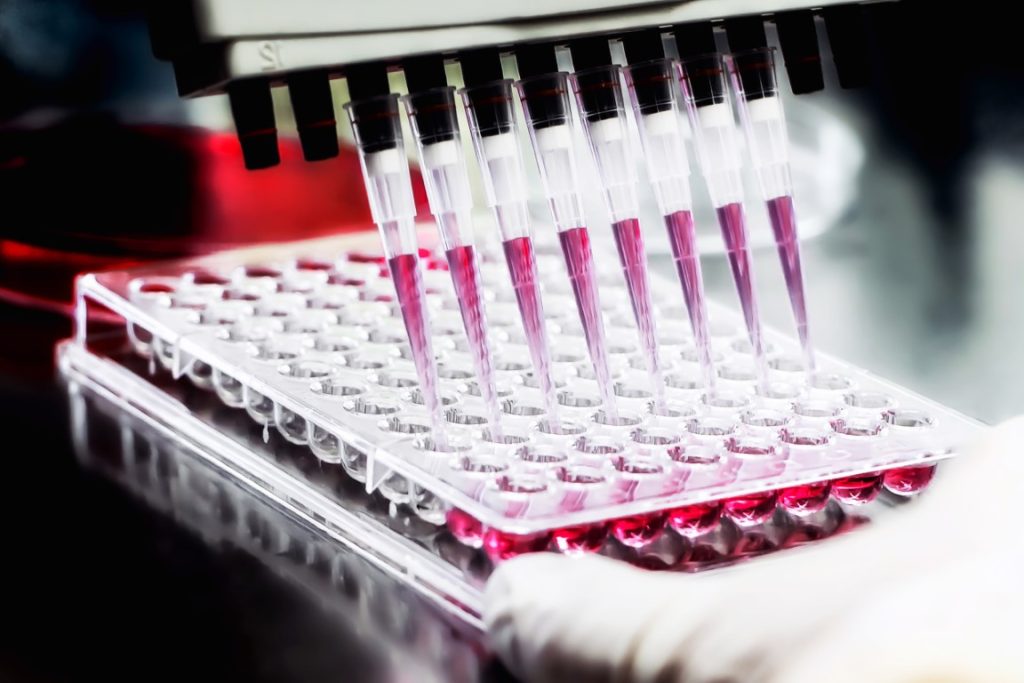
What is the role of biomedical scientists?
They use complex, modern instruments and continuously adopt new methods to increase both the speed and accuracy of diagnostic procedures.
Their responsibilities include continuous monitoring of laboratory performance, rigorous quality control, and adherence to safety standards.
Modern biomedical science relies on computerized, sophisticated automated systems, high-resolution microscopes, and other advanced laboratory technologies. Once results are issued, further patient management may include conservative, surgical, internal medicine, specialist, or therapeutic interventions.
Each biomedical scientist is required to sign off on the findings they produce—this signature carries both professional and legal accountability for the accuracy of the analysis.
Biomedical scientists actively contribute to healthcare reform, education, professional development, research, and the implementation of new diagnostic methods. Like all healthcare professionals, they are required to pursue lifelong education.
They are involved in the training of students within their own field and support the education of other healthcare professionals. They provide patients with information that falls within their professional competencies and responsibilities.
Without the work of biomedical scientists and the biomedical science profession as a whole, the diagnosis of disease, identification of its causes, and evaluation of treatment outcomes would not be possible.
